
Stroke Emergency Help: Brain Stroke Symptoms in Elderly
Learn early brain stroke symptoms in elderly people and what to do immediately. Fast action saves lives. Call Care247 at 1800 2021 247 for stroke emergency help.

Follow & Share
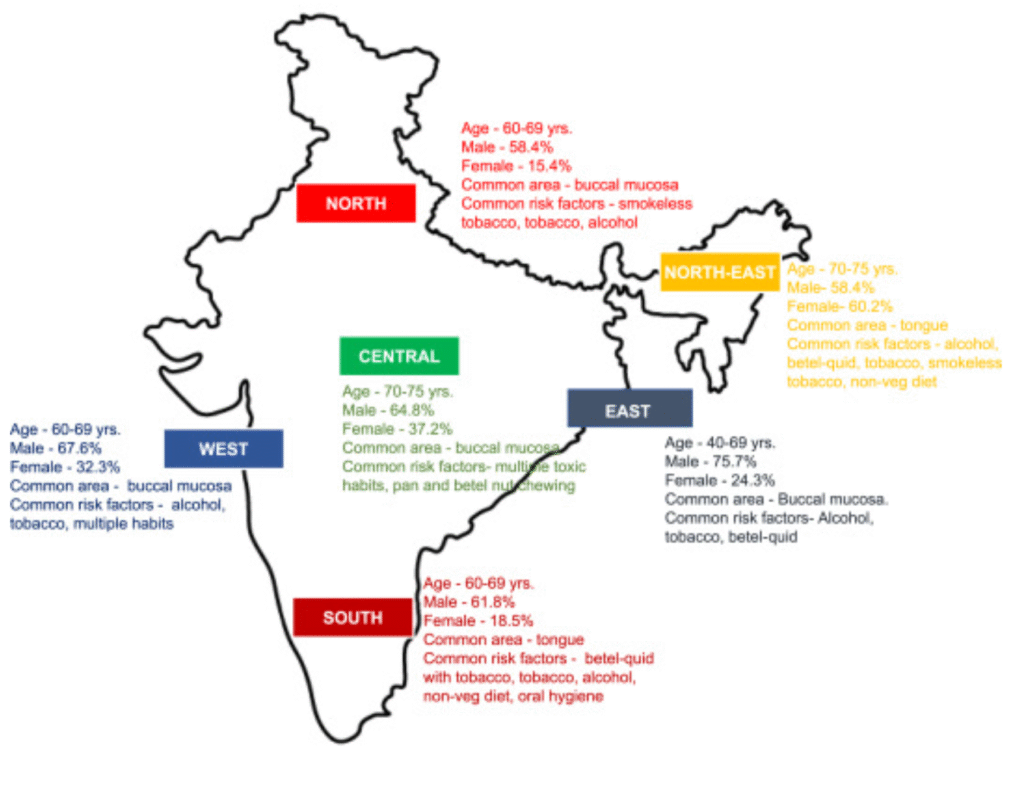
Oral cancer is quickly becoming a major health problem globally. It ranks the top three of all cancers in India and accounts for ~30 percent of all cancers reported. Every 20 out of 100,000 population is suffering with oral cancer. Oral cancer usually gets diagnosed in later stages which makes it more alarming since the disease has already advanced and treatment outcomes less effective, low and expensive. In India, specifically, the population affected more belongs to low socioeconomic section due to a higher risk of exposure to raft toes like tobacco chewing, these population usually present at later stages when the disease has already advanced thus making an comparatively easily treatable cancer subtype a lot difficult to treat and further reducing chances of survival.

Ø Tobacco use – cigarette, pipe and cigar, electronic cigarettes, vape, chewing tobacco
Ø Heavy alcohol use also increases the risk and using tobacco and alcohol both further amplifies the risk
Ø Sexually transmitted infection with HPV virus (human papilloma virus) has been associated with oral cancers
Ø Risk increases with increase in age, >40 yrs of age is most susceptible, but researches in India have revealed a higher incidence in even younger population due to heavy misuse of tobacco
Ø Unprotected sun exposure can cause lip cancer, always use spf 30+ for sun protection
Ø One can also inherit certain gene defects that have a high risk of mouth and middle throat cancer
If you have the following symptoms for more than two weeks seek immediate medical attention
A sore, irritation, lump or thick patch in your mouth, lip, or throat.
A white or red patch in your mouth.
Persistent sore throat, a feeling that something is caught in your throat, or hoarseness or loss of your voice.
A lump in the neck.
Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking.
Difficulty moving your jaw or tongue.
Swelling of your jaw that causes dentures to fit poorly or become uncomfortable.
Pain or bleeding in the mouth.
Numbness in your tongue or other areas of your mouth.
Ear pain.
Self examination is considered one of the most effective methods of oral cancer –
Neck – Run your fingers under your jaw and feel along the large muscle of either side of neck using the fingertips of your fingers. Notice any swellings or if you feel the same on both sides.
Lips & Gums – Using your index, middle fingers and thumb to feel the inside of your mouth. Pull your upper lip upwards and bottom lip downwards to look inside for any sores or changes in colour. Use your thumb and forefinger to feel around and inside your lips checking for any lumps, bumps or changes in texture.
Cheeks – Open your mouth and pull your cheeks away, one side at a time, with your finger to look inside. Look for any red or white patches. Use your finger in the cheek to check for ulcers, lumps or tenderness. Repeat on the other side. Your tongue can be helpful to locate sore areas, ulcers or rough patches.
Tongue – Gently pull out your tongue and look at one side first and then the other. Look for any swelling, ulcer or change in colour. Examine the underside of your tongue by lifting the tip of your tongue to the roof of your mouth.
Floor of mouth – Lift your tongue up and look underneath then look at the floor of your mouth for any colour changes that are unusual. Gently press your finger along the floor of your mouth and underside your tongue to feel for any lumps, swellings or ulcer.
Roof of mouth – Tilt back your head and open your mouth wide to check the roof of your mouth. Look to see if there are changes in colour or ulcers. Check for changes in texture with your finger.
1} Squamous cell carcinoma:- the most prevalent type arising from the flat, scale like cellsthat line in mouth. It is the most common diagnosis in oral malignancies.
2} verrucous carcinoma:- a low grade of variant of squamous cell carcinoma that grows slowly but can still invade surrounding tissues.
3} Minor salivary gland carcinoma:- Cancers that develop in small salivary gland located throughout the oralcavity. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most common type in this category.
4} Lymphoma:- A type of cancer that effects the lymphatic system , which can sometime occur in soft tissues of mouth.
a] Physical examination of the mouth and throat.
b] Biopsy: Removing a small tissue from the affected site and sending it to the lab for testing.
c] Imaging tests such as X rays, Ct scans, or MRI to determine spread.
d] Endoscopy to view deeper areas of the throat.
Treatment depends on the stage and location of the cancer:
1. Surgery: To remove the tumor and affected tissues.
2. Radiation therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
3. Chemotherapy: Drugs to destroy or slow the growth of cancer cells.
4. Targeted therapy or immunotherapy: Helps the immune system fight cancer cells.
Rehabilitation such as speech therapy and dietary counseling may be needed after treatment.
Oral cancers are preventive and treatable if detected early. Awareness and regular screening is most useful and powerful remedy. Protecting your own mouth and your life by making healthy choices in your daily life.
Follow Care247 for more such insights

Learn early brain stroke symptoms in elderly people and what to do immediately. Fast action saves lives. Call Care247 at 1800 2021 247 for stroke emergency help.

Worried about your parents’ health in India while living abroad? This NRI guide answers emergency care, home care, hospital, and elderly support concerns.

Know the real duties of a senior citizen care taker, what they do, what they don’t, and how Care247 supports elders at home. Call 1800 2021 247 to book.